Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of solubility rules with our comprehensive Solubility Rules Chem Worksheet 15 1 Answer Key. This meticulously crafted guide unlocks the secrets of solubility, empowering you to decipher the behavior of chemical compounds in various environments.
Immerse yourself in a world of ions, reactions, and applications, gaining invaluable insights that extend beyond the classroom and into the fascinating world of chemistry.
Delve into the intricacies of solubility rules, unraveling the factors that govern the dissolution and precipitation of substances. Explore the interplay between temperature, pressure, and pH, discovering their profound impact on solubility. Equip yourself with a deep understanding of how solubility rules shape chemical reactions, predicting products and unraveling the mysteries of equilibrium.
Overview of Solubility Rules: Solubility Rules Chem Worksheet 15 1 Answer Key
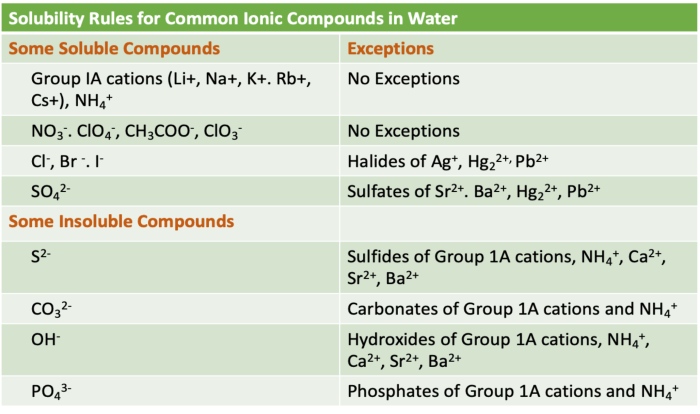
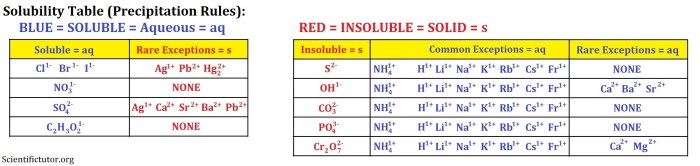
Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, forming a homogeneous mixture. Solubility rules provide guidelines to predict whether a compound will dissolve in water or not. These rules are based on the chemical properties of ions and their interactions with water molecules.
Comprehensive List of Solubility Rules:
- All Group 1 cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) are soluble.
- All Group 2 cations (Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+) are soluble, except for BaSO4.
- All ammonium (NH4+) ions are soluble.
- All nitrate (NO3-) ions are soluble.
- All chloride (Cl-) ions are soluble, except for AgCl, PbCl2, and Hg2Cl2.
- All bromide (Br-) ions are soluble, except for AgBr, PbBr2, and Hg2Br2.
- All iodide (I-) ions are soluble, except for AgI, PbI2, and Hg2I2.
- All sulfate (SO42-) ions are soluble, except for BaSO4 and SrSO4.
- All carbonate (CO32-) ions are insoluble, except for Na2CO3, K2CO3, and CaCO3.
- All phosphate (PO43-) ions are insoluble, except for Na3PO4, K3PO4, NH43PO4, and the salts of the Group 1 cations.
- All hydroxide (OH-) ions are insoluble, except for the salts of the Group 1 cations.
Factors Affecting Solubility:
In addition to the solubility rules, several factors influence the solubility of a compound:
- Temperature:Solubility generally increases with temperature.
- Pressure:Solubility of gases in liquids increases with pressure.
- pH:Solubility of some compounds depends on the pH of the solution.
FAQs
What are the key solubility rules?
Solubility rules provide guidelines for predicting the solubility of ionic compounds in water. Common cations and anions are classified as soluble or insoluble, with exceptions noted.
How can I use solubility rules to solve chemistry problems?
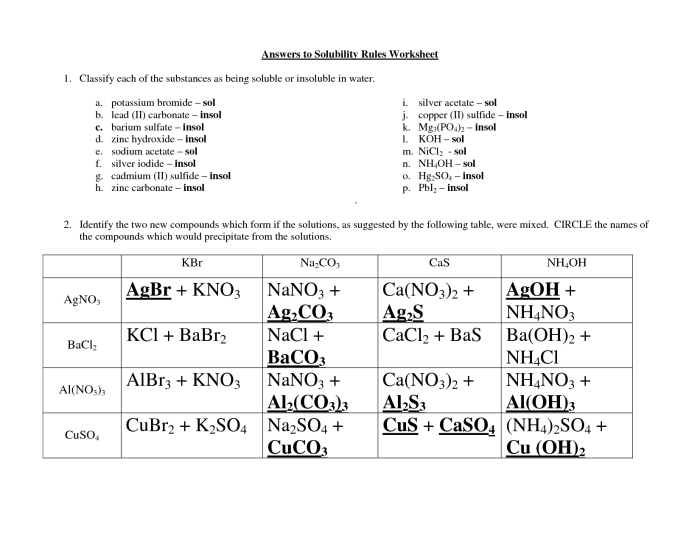
Solubility rules enable the prediction of whether a chemical reaction will result in the formation of a precipitate. By analyzing the solubility of the reactants and products, you can determine the likelihood of a reaction occurring.
What are some real-world applications of solubility rules?
Solubility rules find applications in various industries, including water treatment, where they guide the removal of impurities and contaminants. In food processing, solubility plays a role in preserving and enhancing flavors, textures, and colors.