Delving into the realm of lion phylogeny, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricate connections that shape the evolutionary history and genetic diversity of these magnificent creatures. Embarking with the lion phylogeny finding connections answer key, we explore the fascinating tapestry of lion evolution, tracing their lineage through time and across continents.
Our exploration delves into the genetic makeup of lion subspecies, uncovering the unique adaptations that have allowed them to thrive in diverse habitats. We examine their comparative anatomy and morphology, revealing the remarkable physical traits that reflect their predatory lifestyle and social dynamics.
Lion Phylogeny: A Comprehensive Overview
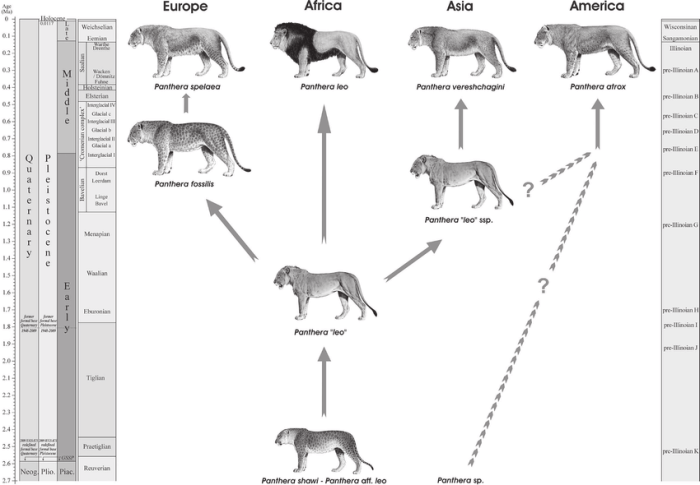
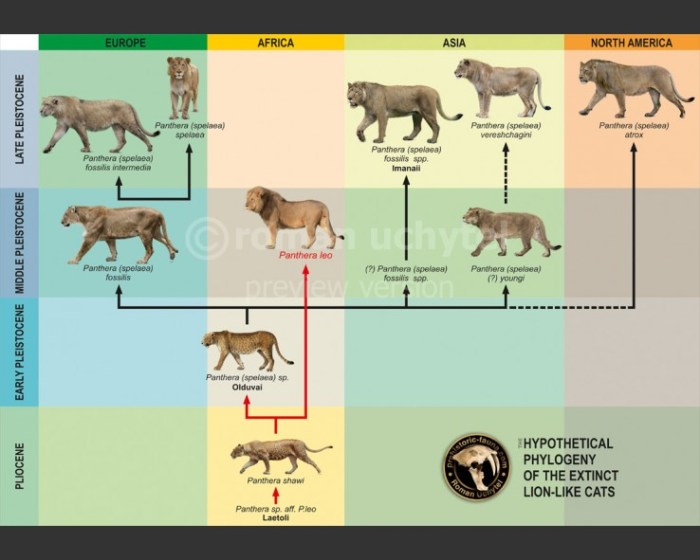
Lion phylogeny encompasses the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among lion species. Understanding lion phylogeny is crucial for unraveling the complex origins and adaptations that have shaped the lion’s unique characteristics and ecological role.
The evolutionary timeline of lions can be traced back millions of years, with the earliest lion ancestors appearing during the Miocene epoch. Over time, these ancestors diversified into various species, including the extant lion species: the African lion (Panthera leo) and the Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica).
Genetic analysis plays a pivotal role in tracing lion ancestry and relationships. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and nuclear DNA studies have provided valuable insights into lion population structure, genetic diversity, and historical gene flow. These analyses have helped identify distinct lion subspecies and shed light on their evolutionary history.
Subspecies and Genetic Diversity
Lions are classified into several subspecies based on their geographic distribution and unique characteristics. The recognized lion subspecies include:
- African lion (Panthera leo leo)
- Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica)
- Barbary lion (Panthera leo leo)
- Cape lion (Panthera leo melanochaita)
- Congo lion (Panthera leo azandica)
- Katanga lion (Panthera leo bleyenberghi)
- Masai lion (Panthera leo massaicus)
- Natal lion (Panthera leo krugeri)
- Transvaal lion (Panthera leo krugeri)
- West African lion (Panthera leo senegalensis)
Genetic diversity within and between lion subspecies varies due to factors such as geographic isolation, historical events, and selective pressures. Genetic diversity is essential for lion conservation and survival, as it provides the raw material for adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Comparative Anatomy and Morphology, Lion phylogeny finding connections answer key
Lions exhibit diverse anatomical and morphological adaptations related to their habitat and behavior. Comparative studies of different lion subspecies have revealed:
- Skeletal adaptations:Lions have robust skeletons with powerful muscles, allowing for efficient hunting and territorial defense.
- Musculature:Lions possess well-developed muscles, particularly in their forelimbs and shoulders, which enable them to take down large prey.
- Dentition:Lions have specialized teeth, including large canines for killing prey and premolars for shearing meat.
- Sexual dimorphism:Male lions are typically larger than females, with distinct manes that play a role in social signaling and mate selection.
Behavioral Ecology and Social Structure
Lions exhibit complex social behavior and organization. They live in prides, which are typically composed of related females, their offspring, and one or more adult males. Pride dynamics involve cooperative hunting, territorial defense, and social interactions.
Environmental factors and resource availability influence lion behavior and social interactions. For example, in areas with abundant prey, lions may form larger prides, while in areas with limited resources, they may live in smaller groups or as solitary individuals.
Conservation Status and Threats
Lions face various conservation challenges, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization fragments lion populations and disrupts their natural behavior.
Poaching for body parts and trophies remains a major threat to lions. Additionally, human-wildlife conflict arises when lions come into contact with human settlements, leading to livestock depredation and potential danger to humans.
Conservation strategies for lions involve habitat protection, anti-poaching measures, and community-based conservation initiatives. International collaboration and transboundary conservation efforts are crucial for protecting lion populations and their habitats.
Popular Questions: Lion Phylogeny Finding Connections Answer Key
What is the significance of lion phylogeny?
Lion phylogeny provides a framework for understanding the evolutionary history and relationships among lion populations, shedding light on their genetic diversity and adaptations.
How does genetic analysis contribute to lion phylogeny?
Genetic analysis of lion DNA allows researchers to trace ancestry, identify subspecies, and assess genetic diversity, providing valuable insights into lion evolution and conservation.
What are the key adaptations observed in lion subspecies?
Lion subspecies exhibit adaptations related to their habitat and behavior, such as variations in mane size and color, body size, and hunting strategies, reflecting their ecological niches.