Bias can be evident in one’s analysis of objective truth – Bias, an inherent aspect of human cognition, can profoundly influence our analysis of objective truth. Understanding the nature and implications of bias is paramount for fostering critical thinking, promoting ethical analysis, and navigating the complexities of decision-making in an increasingly interconnected world.
This discourse will delve into the multifaceted relationship between bias and objective analysis, exploring the impact of personal biases on the interpretation of facts, identifying techniques for mitigating bias, and highlighting the ethical implications of biased analysis. By shedding light on the pervasive influence of bias, we aim to equip readers with the tools and strategies necessary for navigating the challenges of objective analysis and striving for greater intellectual rigor.
The Impact of Biases on Objective Analysis: Bias Can Be Evident In One’s Analysis Of Objective Truth
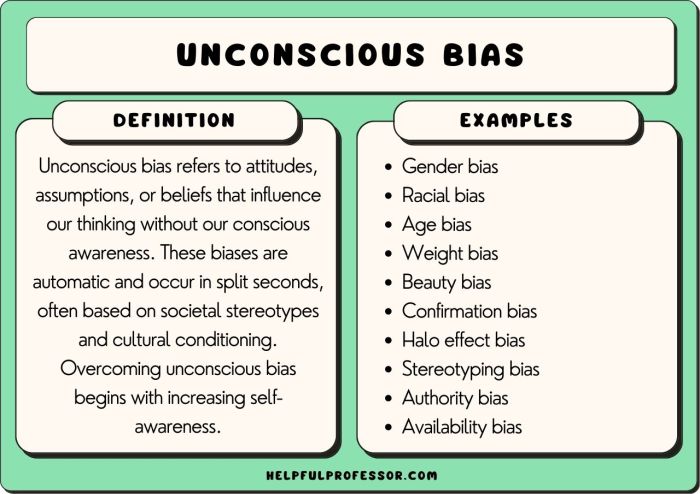
Biases are cognitive distortions that influence how individuals perceive and interpret information. They can have a profound impact on the analysis of objective truth, leading to distorted conclusions and flawed decision-making.
Personal biases stem from an individual’s beliefs, values, and experiences. These biases can lead to selective attention, where individuals focus on information that confirms their existing beliefs while ignoring or downplaying contradictory evidence. Additionally, biases can influence how individuals interpret data, leading to conclusions that align with their preconceived notions.
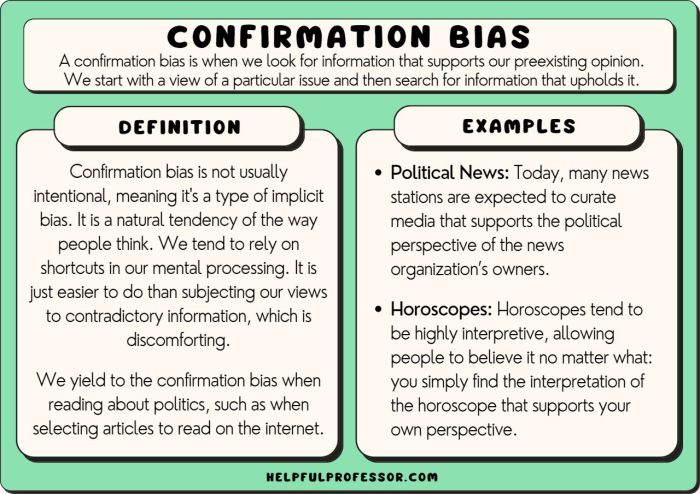
For example, an investor with a strong belief in a particular stock may be more likely to seek out and interpret information that supports their investment, while ignoring potential risks. This bias can lead to an overestimation of the stock’s value and potentially disastrous investment decisions.
Challenges of Overcoming Biases, Bias can be evident in one’s analysis of objective truth
Overcoming biases in analysis is a challenging task. Biases are often deeply ingrained and may not be consciously recognized. Additionally, the cognitive effort required to critically examine one’s own biases can be significant, and individuals may be reluctant to engage in such self-reflection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common types of biases that can influence objective analysis?
Confirmation bias, availability bias, framing bias, and anchoring bias are among the most prevalent types of biases that can distort our analysis.
How can we identify and mitigate the effects of bias in our analysis?
Techniques such as critical self-reflection, seeking diverse perspectives, and employing rigorous methodologies can help us identify and mitigate the effects of bias.
Why is it important to consider the ethical implications of biased analysis?
Biased analysis can lead to flawed conclusions, unfair judgments, and unethical decision-making, which can have significant consequences for individuals and society as a whole.