Energy webquest nonrenewable and renewable energy – Embarking on an educational journey with the Energy WebQuest, we delve into the realm of nonrenewable and renewable energy sources, unveiling their distinct characteristics, advantages, and implications for our planet’s future. Prepare to broaden your understanding of energy consumption, conservation, sustainability, and the crucial role of energy policies and technologies in shaping our energy landscape.
As we navigate this comprehensive guide, we will examine the finite nature of nonrenewable energy sources such as fossil fuels, contrasting them with the replenishable potential of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. We will explore the intricate web of factors influencing global energy consumption, unraveling the environmental impacts associated with energy production and consumption.
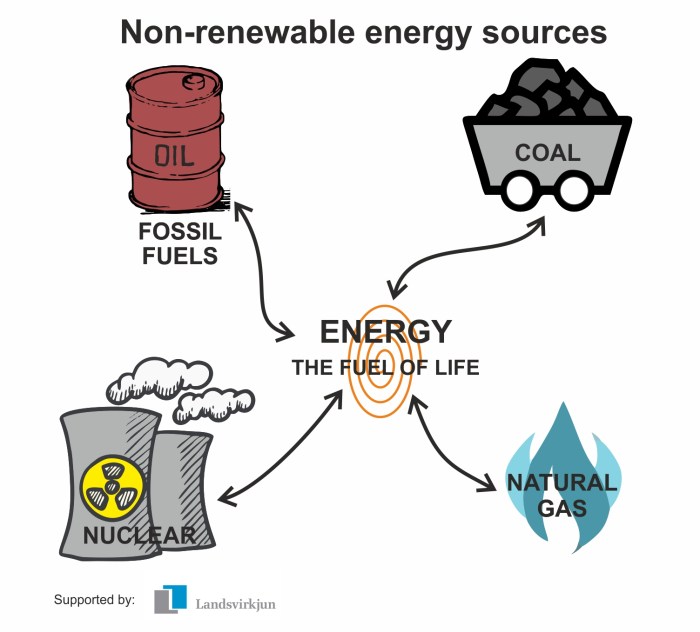
Nonrenewable Energy Sources: Energy Webquest Nonrenewable And Renewable Energy

Nonrenewable energy sources are finite resources that cannot be replenished on a human timescale. These sources include fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as nuclear energy.
Fossil fuels are formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals that have been buried and converted to coal, oil, or natural gas over millions of years. Nuclear energy is produced by splitting atoms in a process called nuclear fission.
Advantages of Nonrenewable Energy Sources
- Reliable: Nonrenewable energy sources are generally reliable and can be used to generate electricity on demand.
- Affordable: Nonrenewable energy sources are often relatively affordable compared to renewable energy sources.
- High energy density: Nonrenewable energy sources have a high energy density, meaning they can store a lot of energy in a small space.
Disadvantages of Nonrenewable Energy Sources
- Finite: Nonrenewable energy sources are finite and will eventually run out.
- Pollution: The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
- Climate change: The burning of fossil fuels is a major contributor to climate change.
- Renewable: Renewable energy sources are renewable and will never run out.
- Clean: Renewable energy sources do not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
- Sustainable: Renewable energy sources are sustainable and can be used to generate electricity without harming the environment.
- Intermittent: Renewable energy sources are intermittent and cannot always be relied upon to generate electricity when needed.
- Expensive: Renewable energy sources are often more expensive than nonrenewable energy sources.
- Land use: Renewable energy sources can require a lot of land to generate electricity.
Renewable Energy Sources

Renewable energy sources are energy sources that can be replenished naturally on a human timescale. These sources include solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass.
Solar energy is produced by capturing the sun’s energy using photovoltaic cells or solar thermal collectors. Wind energy is produced by capturing the energy of the wind using turbines. Hydropower is produced by capturing the energy of flowing water using dams and turbines.
Geothermal energy is produced by capturing the heat of the earth’s core using geothermal wells. Biomass is produced by burning organic matter, such as wood or crops.
Benefits of Renewable Energy Sources, Energy webquest nonrenewable and renewable energy
Limitations of Renewable Energy Sources
Energy Consumption

Global energy consumption has been increasing steadily for decades. In 2020, the world consumed approximately 586 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu) of energy. The United States is the world’s largest energy consumer, accounting for about 20% of global energy consumption.
There are a number of factors that influence energy consumption, including population growth, economic growth, and technological change. Population growth leads to increased demand for energy, as more people need to be heated, cooled, and transported. Economic growth also leads to increased energy consumption, as businesses and industries need more energy to operate.
Technological change can both increase and decrease energy consumption. For example, the development of more efficient appliances and lighting can reduce energy consumption, while the development of new technologies, such as electric vehicles, can increase energy consumption.
Environmental Impacts of Energy Consumption
The burning of fossil fuels to generate electricity releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to climate change. Climate change can have a number of negative impacts on the environment, including rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, and changes in plant and animal life.
Top FAQs
What is the primary distinction between nonrenewable and renewable energy sources?
Nonrenewable energy sources, such as fossil fuels, are finite and will eventually deplete, while renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are replenished naturally and can be sustainably utilized.
What are the key advantages of renewable energy sources?
Renewable energy sources offer numerous advantages, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower operating costs, diversification of energy supply, and job creation in the clean energy sector.
How can energy conservation contribute to sustainability?
Energy conservation practices, such as energy-efficient appliances, insulation, and behavioral changes, can significantly reduce energy consumption, minimizing environmental impacts and promoting sustainability.