Polarity and intermolecular forces gizmo answers – Delving into the realm of polarity and intermolecular forces, this comprehensive exploration unveils the intricacies of molecular interactions and their profound impact on matter’s behavior. Embarking on a journey guided by the Gizmo simulation, we unravel the secrets of polarity and intermolecular forces, unlocking their practical applications across diverse scientific disciplines.
Polarity, the uneven distribution of charge within a molecule, and intermolecular forces, the forces acting between molecules, play a pivotal role in shaping the physical properties and behavior of matter. Through the Gizmo simulation, we delve into the dynamics of these forces, investigating their influence on properties such as boiling point, melting point, and solubility.
Define Polarity and Intermolecular Forces: Polarity And Intermolecular Forces Gizmo Answers

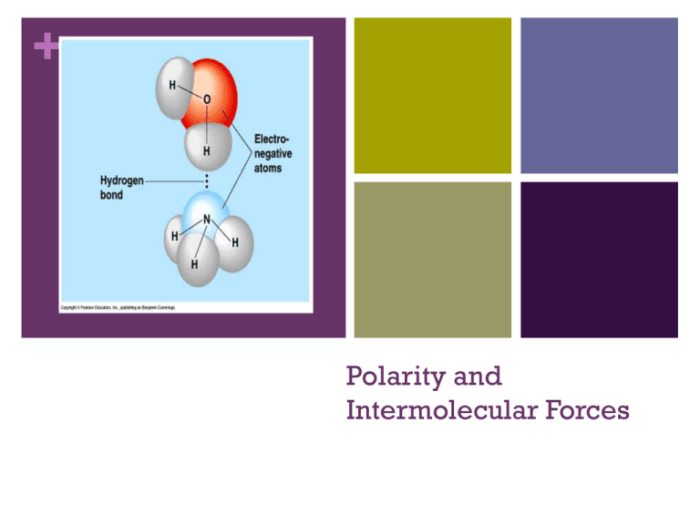
Polarity refers to the separation of electric charges within a molecule. It occurs when electrons are unequally distributed, resulting in a positive end and a negative end. Polar molecules have a permanent dipole moment, while nonpolar molecules have no dipole moment.
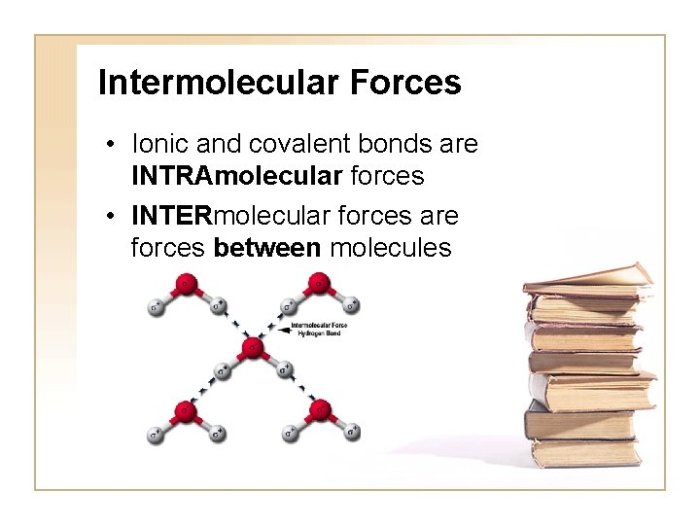
Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces between molecules. They include:
- Dipole-dipole forces: occur between polar molecules with permanent dipole moments.
- Hydrogen bonding: a special type of dipole-dipole force that occurs between molecules with hydrogen atoms bonded to small, highly electronegative atoms (F, O, N).
- London dispersion forces: occur between all molecules, regardless of polarity. They are caused by the temporary, instantaneous polarization of molecules.
Gizmo Simulation
The Gizmo simulation allows you to investigate the polarity and intermolecular forces of different molecules. You can:
- Select different molecules from a drop-down menu.
- Observe the molecular structure and polarity.
- Measure the strength of the intermolecular forces.
- Predict the physical properties of the molecules.
To analyze the simulation results, consider the following:
- The dipole moment of a molecule is a measure of its polarity.
- The strength of the intermolecular forces depends on the polarity of the molecules.
- The physical properties of a substance are influenced by the strength of the intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Intermolecular forces affect the physical properties of substances:
- Boiling point:The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the boiling point.
- Melting point:The stronger the intermolecular forces, the higher the melting point.
- Solubility:Polar molecules are generally more soluble in polar solvents, while nonpolar molecules are more soluble in nonpolar solvents.
| Intermolecular Force | Strength | Boiling Point | Melting Point | Solubility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipole-dipole | Strong | High | High | Polar solvents |
| Hydrogen bonding | Very strong | Very high | Very high | Polar solvents |
| London dispersion | Weak | Low | Low | Nonpolar solvents |
Applications of Polarity and Intermolecular Forces, Polarity and intermolecular forces gizmo answers
Understanding polarity and intermolecular forces has practical applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Predicting chemical reactions, designing new materials, and understanding molecular interactions.
- Biology:Understanding the structure and function of biomolecules, such as proteins and DNA.
- Materials science:Developing new materials with specific properties, such as strength, durability, and conductivity.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of polarity in molecular interactions?
Polarity governs the strength and nature of intermolecular forces, influencing molecular interactions and behavior.
How does the Gizmo simulation enhance the understanding of intermolecular forces?
The Gizmo simulation provides an interactive platform to visualize and investigate intermolecular forces, allowing for a deeper comprehension of their dynamics.
What practical applications stem from understanding polarity and intermolecular forces?
These forces find applications in fields such as chemistry (solubility and reaction mechanisms), biology (protein folding and enzyme activity), and materials science (polymer design and drug delivery).