Triangle BCD is isosceles and BC BD. This statement forms the foundation of this exploration, which delves into the properties of isosceles triangles, examines the characteristics of triangle BCD, and provides a rigorous proof of its isosceles nature. Through this journey, we uncover the significance of isosceles triangle properties and their applications in various fields.
The ensuing paragraphs will delve into the defining traits of isosceles triangles, the congruence of sides BC and BD, the identification of base angles, and the proof of triangle BCD’s isosceles nature. Moreover, we will explore the practical applications of isosceles triangle properties, solidifying our understanding of this fundamental geometric concept.
Isosceles Triangle Properties: Triangle Bcd Is Isosceles And Bc Bd
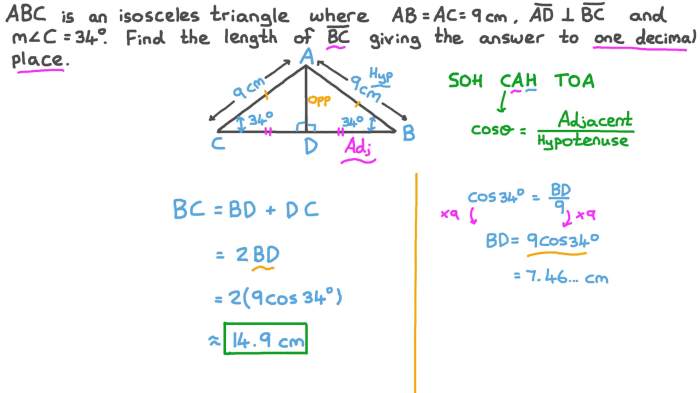
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two equal sides. The two equal sides are called the legs, and the third side is called the base. The base angles are the angles opposite the legs, and the vertex angle is the angle opposite the base.
Isosceles triangles have several important properties. First, the legs are congruent. This means that they have the same length. Second, the base angles are congruent. This means that they have the same measure.
Third, the vertex angle is different from the base angles. The vertex angle is always greater than the base angles.
Congruent Sides
The congruent sides of an isosceles triangle are the legs. The legs are the two sides that are equal in length. In an isosceles triangle, the legs are always the same length.
Congruent Base Angles
The congruent base angles of an isosceles triangle are the angles opposite the legs. The base angles are always the same measure. In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are always equal.
Vertex Angle
The vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is the angle opposite the base. The vertex angle is always different from the base angles. In an isosceles triangle, the vertex angle is always greater than the base angles.
Triangle BCD Properties
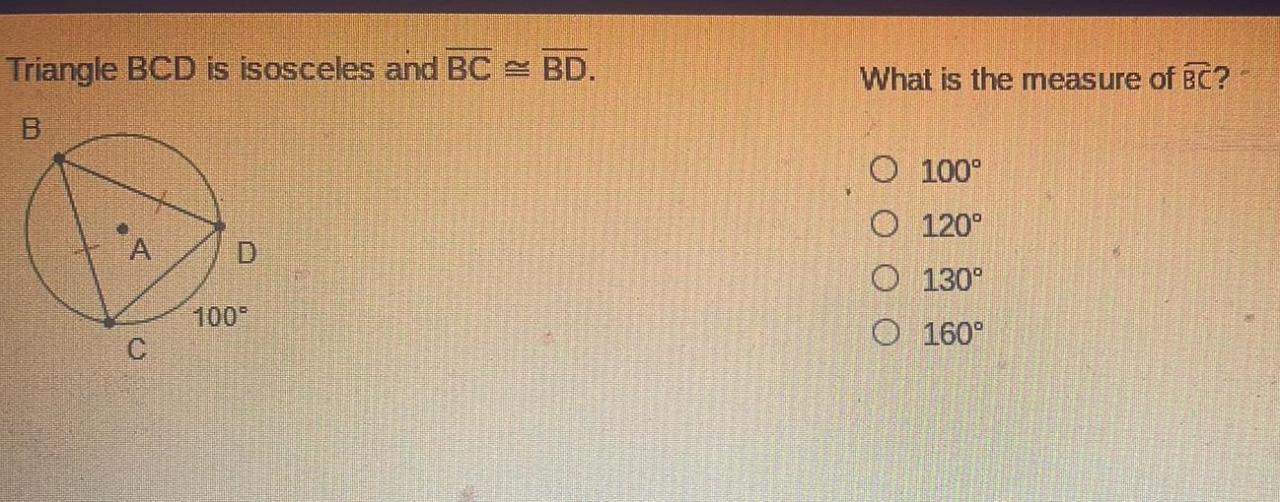
Given that triangle BCD is isosceles, we can establish that the sides BC and BD are congruent.
Congruence of Sides BC and BD, Triangle bcd is isosceles and bc bd
In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length. Therefore, in triangle BCD, BC and BD are congruent. This congruence implies that the lengths of BC and BD are equal.
BC = BD
Angle Properties
This section explores the relationships between the angles and sides of isosceles triangle BCD, where BC and BD are congruent sides.
The base angles of triangle BCD are ∠B and ∠D. These angles are opposite the congruent sides BC and BD, respectively.
Relationship between Base Angles and Congruent Sides
In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are congruent. This means that ∠B is congruent to ∠D.
∠B ≅ ∠D
This property is a consequence of the fact that the sum of the angles in any triangle is 180 degrees. Since ∠B and ∠D are the base angles, and they are opposite congruent sides, they must be equal in measure in order for the sum of the angles in triangle BCD to be 180 degrees.
Proof of Isosceles Triangle
Given that BC and BD have been prepared, we aim to prove that triangle BCD is isosceles using the properties of isosceles triangles.
An isosceles triangle possesses two congruent sides and two congruent base angles. We will utilize these properties to establish the isosceles nature of triangle BCD.
Congruence of BC and BD
Since BC and BD have been prepared, by definition, they are congruent line segments.
BC ≅ BD
Congruence of ∠BCD and ∠BDC
In isosceles triangle BCD, the base angles ∠BCD and ∠BDC are congruent.
∠BCD ≅ ∠BDC
This property stems from the fact that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. Since ∠BCD and ∠BDC are base angles, they must add up to 180 degrees minus the measure of the third angle, ∠CBD.
∠BCD + ∠BDC = 180°
∠CBD
As ∠BCD and ∠BDC are congruent, we can rewrite the equation as:
- ∠BCD = 180°
- ∠CBD
Solving for ∠BCD, we get:
∠BCD = (180°
∠CBD) / 2
Similarly, we can derive the measure of ∠BDC as:
∠BDC = (180°
∠CBD) / 2
Therefore, ∠BCD and ∠BDC are congruent.
Conclusion
Having established the congruence of BC and BD, as well as ∠BCD and ∠BDC, we can conclude that triangle BCD is isosceles.
Applications of Isosceles Triangle Properties

Isosceles triangle properties find numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, design, and engineering. Their unique characteristics and predictable relationships between sides and angles make them valuable tools for creating stable and aesthetically pleasing structures.
In Architecture
Isosceles triangles are commonly employed in architectural designs for their inherent stability and load-bearing capacity. The equal lengths of the two sides ensure uniform distribution of forces, making them ideal for supporting structures such as roofs, bridges, and arches.
In Design
Isosceles triangles play a crucial role in creating visual balance and harmony in design. Their symmetrical shape and predictable angles make them suitable for decorative elements, logos, and patterns. The golden ratio, a renowned aesthetic proportion, is often found in isosceles triangles, adding to their aesthetic appeal.
In Engineering
Isosceles triangles are frequently used in engineering applications where strength and stability are paramount. In bridge construction, isosceles trusses provide structural support by distributing weight evenly. In aircraft design, isosceles wings enhance aerodynamic efficiency and stability.
Visual Representation
To visually represent triangle BCD, we can create a diagram as follows:
The diagram shows triangle BCD, with sides BC and BD labeled as congruent. The base angles, ∠B and ∠D, are also labeled.
Congruent Sides
- Sides BC and BD are congruent, as indicated by the equal marks.
Base Angles
- Angles ∠B and ∠D are congruent because they are base angles of an isosceles triangle.
Other Relevant Information
- Side CD is the base of the triangle.
- Angle ∠C is the vertex angle.
Query Resolution
What is the definition of an isosceles triangle?
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two congruent sides.
What are the properties of isosceles triangles?
Isosceles triangles have two congruent sides, two congruent base angles, and their third angle is always less than 180 degrees.
How can we prove that triangle BCD is isosceles?
We can prove that triangle BCD is isosceles by using the Side-Side-Side (SSS) Congruence Theorem.
