What was a trench block? Dive into the intriguing world of trench warfare, where these unassuming concrete structures played a pivotal role in shaping the course of battle. From their humble origins to their lasting impact, this comprehensive guide unravels the secrets of these enigmatic fortifications.
Trench blocks, also known as trench blocks, were ubiquitous during World War I, serving as the building blocks of elaborate trench systems that crisscrossed the war-torn landscapes of Europe. These seemingly simple concrete blocks held immense strategic significance, influencing the ebb and flow of combat and leaving an indelible mark on the nature of warfare.
Definition and Overview: What Was A Trench Block

A trench block is a defensive structure used in warfare to create a fortified position. It is typically made of concrete, metal, or wood and is designed to provide cover and protection for troops from enemy fire.
Trench blocks were first used during World War I, when they were employed by both sides to create defensive lines in the trenches. They were also used in World War II and other conflicts.
Types of Trench Blocks
There are many different types of trench blocks, each with its own unique purpose and design. Some of the most common types include:
- Sandbags: Sandbags are the simplest and most common type of trench block. They are filled with sand or other materials and can be stacked to create a variety of defensive structures.
- Concrete blocks: Concrete blocks are more durable than sandbags and can provide better protection from enemy fire. They are often used to create permanent defensive positions.
- Metal blocks: Metal blocks are the most durable type of trench block and can provide the best protection from enemy fire. They are often used to create fortified positions in areas where there is a high risk of attack.
Design and Construction
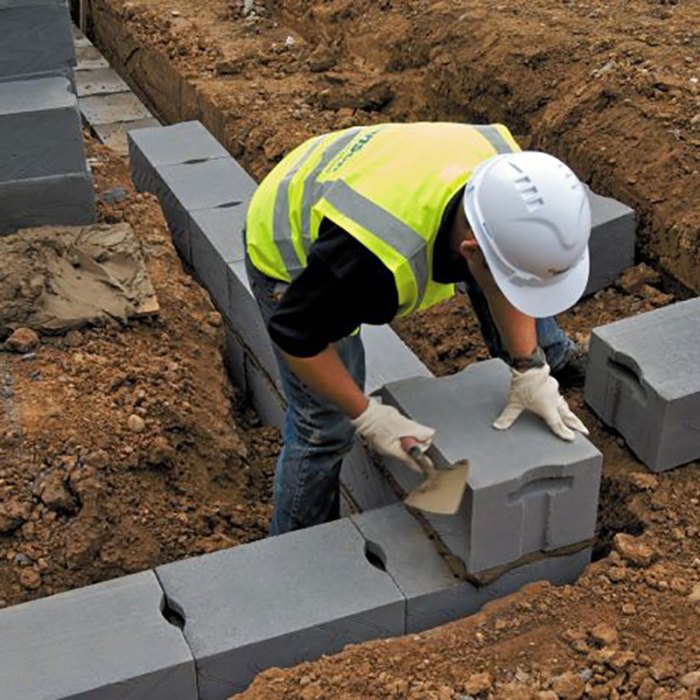

Trench blocks, also known as concrete blocks, are modular elements used to construct protective structures such as bunkers, fortifications, and barriers.
These blocks are designed to withstand various environmental conditions and military threats, providing reliable protection for personnel and equipment.
Materials
Trench blocks are typically made of high-strength concrete, which is a composite material consisting of cement, aggregates (such as gravel and sand), and water.
Reinforcement materials, such as steel bars or fibers, are often incorporated to enhance the strength and durability of the blocks.
A trench block was a system of defensive fortifications used in World War I. To learn more about trench blocks, check out abeka algebra 2 quiz 34 . Trench blocks were typically constructed from wood or sandbags and were designed to provide cover from enemy fire.
Manufacturing
Trench blocks are manufactured using various techniques, including:
- Dry-cast method:Involves mixing the concrete components in a dry state and then compacting them into molds using hydraulic or mechanical pressure.
- Wet-cast method:Involves mixing the concrete components with water to form a slurry that is poured into molds and allowed to cure.
Dimensions and Specifications
Trench blocks come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but common dimensions include:
- Length: 600 mm to 1200 mm
- Width: 200 mm to 400 mm
- Height: 200 mm to 600 mm
The specific dimensions and specifications of trench blocks may vary depending on the intended application and regional standards.
Deployment and Use
Trench blocks were deployed in various ways on the battlefield, depending on the terrain and the tactical situation.
One common method was to create a continuous line of trench blocks, forming a defensive barrier. This was often done in conjunction with barbed wire and other obstacles to create a formidable obstacle to enemy troops.
Strategic Advantages
- Provided cover for troops from enemy fire
- Slowed down and channeled enemy movements
- Protected against artillery bombardments
- Could be used to create obstacles, such as roadblocks and tank traps
Strategic Disadvantages
- Time-consuming and labor-intensive to deploy
- Could be destroyed by artillery fire or explosives
- Limited mobility once deployed
- Could create a psychological barrier for troops, making them less likely to advance
Examples of Battles, What was a trench block
Trench blocks played a significant role in many battles during World War I, including:
- The Battle of the Somme
- The Battle of Verdun
- The Battle of Passchendaele
Variants and Adaptations

Trench blocks varied in design and construction depending on the army and theater of war. Some armies developed specialized trench blocks for specific purposes, while others modified existing designs to enhance their effectiveness.
Variations in trench blocks included:
Shape and Size
- Rectangular blocks: These were the most common type of trench block, typically measuring around 2 feet long, 1 foot wide, and 6 inches thick.
- Trapezoidal blocks: These blocks had a trapezoidal shape, with a wider base than top. They were designed to provide greater stability and reduce the risk of collapse.
- Irregular blocks: Some armies used irregular-shaped blocks, such as broken bricks or rubble, to fill gaps or create obstacles.
Materials
- Concrete: Concrete was the most widely used material for trench blocks, as it was durable, fire-resistant, and could be easily cast into different shapes.
- Steel: Steel trench blocks were used in some cases, particularly for specialized purposes such as armored bunkers or observation posts.
- Wood: Wooden trench blocks were sometimes used as a temporary measure or in areas where concrete or steel was not available.
Adaptations
- Handles: Some trench blocks were equipped with handles or lifting points to facilitate transportation and placement.
- Reinforcement: Trench blocks could be reinforced with steel rods or wire mesh to increase their strength and durability.
- Embrasures: Embrasures were openings in trench blocks designed for firing weapons. They could be fitted with shutters or covers to protect the occupants from enemy fire.
Impact and Legacy

The introduction of trench blocks profoundly altered the nature of warfare during World War I. Their defensive capabilities transformed the battlefield into a static, trench-bound stalemate, where frontal assaults became increasingly costly and ineffective.
Influence on Military Tactics and Strategies
- Defensive Advantage:Trench blocks provided troops with enhanced protection against enemy fire, reducing casualties and hindering offensive operations.
- Static Warfare:The difficulty in breaching fortified trench lines led to a prolonged period of trench warfare, characterized by limited territorial gains and heavy losses.
- New Combat Techniques:The use of trench blocks necessitated the development of specialized tactics, such as tunneling, sapping, and the use of grenades and flamethrowers.
Historical Legacy and Significance
Trench blocks have left a lasting legacy in modern warfare. Their defensive principles continue to inform the design of fortifications and bunkers, while the lessons learned from trench warfare have shaped military strategies and tactics.
- Battlefield Engineering:Trench blocks demonstrated the importance of defensive fortifications and influenced the development of field engineering techniques.
- Urban Warfare:The tactics and challenges encountered in trench warfare provided valuable insights for urban warfare, where buildings and structures serve as defensive obstacles.
- Legacy of Stalemate:The prolonged stalemate of trench warfare remains a cautionary tale against the dangers of protracted, attrition-based conflicts.
FAQ Compilation
What was the primary purpose of a trench block?
Trench blocks were primarily used to construct defensive fortifications, such as trench walls and bunkers, providing protection for soldiers from enemy fire and shrapnel.
How were trench blocks manufactured?
Trench blocks were typically cast in concrete molds, using a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregate. They were often reinforced with steel rods or wire mesh to enhance their durability.
What were the advantages of using trench blocks?
Trench blocks offered several advantages, including ease of construction, durability, and adaptability. They could be quickly assembled and disassembled, allowing for rapid deployment and redeployment as needed.